|
|
|
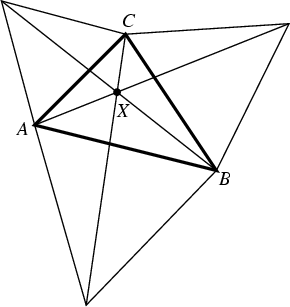
Also known as the first Isogonic Center and the Torricelli Point. In a given
Acute Triangle ![]() , the Fermat point is the point
, the Fermat point is the point ![]() which minimizes the sum of distances from
which minimizes the sum of distances from ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
and
,
and ![]() ,
,
| (1) |
If all Angles of the Triangle are less than 120° (![]() ), then the Fermat point is the
interior point
), then the Fermat point is the
interior point ![]() from which each side subtends an Angle of 120°, i.e.,
from which each side subtends an Angle of 120°, i.e.,
| (2) |
| (3) | |||
| (4) |
The Antipedal Triangle is Equilateral and has Area
| (5) |
Given three Positive Real Numbers ![]() , the ``generalized'' Fermat point is the point
, the ``generalized'' Fermat point is the point ![]() of a
given Acute Triangle
of a
given Acute Triangle ![]() such that
such that
| (6) |
See also Isogonic Centers
References
Courant, R. and Robbins, H. What is Mathematics?, 2nd ed. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1941.
Gallatly, W. The Modern Geometry of the Triangle, 2nd ed. London: Hodgson, p. 107, 1913.
Greenberg, I. and Robertello, R. A. ``The Three Factory Problem.'' Math. Mag. 38, 67-72, 1965.
Honsberger, R. Mathematical Gems I. Washington, DC: Math. Assoc. Amer., pp. 24-34, 1973.
Johnson, R. A. Modern Geometry: An Elementary Treatise on the Geometry of the Triangle and the Circle.
Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, pp. 221-222, 1929.
Kimberling, C. ``Central Points and Central Lines in the Plane of a Triangle.'' Math. Mag. 67, p. 174, 1994.
Kimberling, C. ``Fermat Point.''
http://cedar.evansville.edu/~ck6/tcenters/class/fermat.html.
Mowaffaq, H. ``An Advanced Calculus Approach to Finding the Fermat Point.'' Math. Mag. 67, 29-34, 1994.
Pottage, J. Geometrical Investigations. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1983.
Spain, P. G. ``The Fermat Point of a Triangle.'' Math. Mag. 69, 131-133, 1996.
Tong, J. and Chua, Y. S. ``The Generalized Fermat's Point.'' Math. Mag. 68, 214-215, 1995.
van de Lindt, W. J. ``A Geometrical Solution of the Three Factory Problem.'' Math. Mag. 39, 162-165, 1966.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein